Differentiation of composite function. Chain rule.
Utilities of composite function.
1. Factorization
2. Chain rule in derivation. Application on formulae.
3. Substitution in integration. Application on formulae.
4. ln is the inverse of exponential function and vice versa.
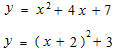
An equation with parenthesis in it is already a kind of composite function.
See distributivity, associativity, commutativity.
That facilitates operations and as differential du, dx, dy, etc., unit of graduations in the coordinates system of the exterior function changes its relational width.
Here is a machine which would multiply by 3 the money you put in. This machine is named g .
And another machine, h , which would make twice more the money you put in. If you put the money which came out of g into h , what would you get after all?
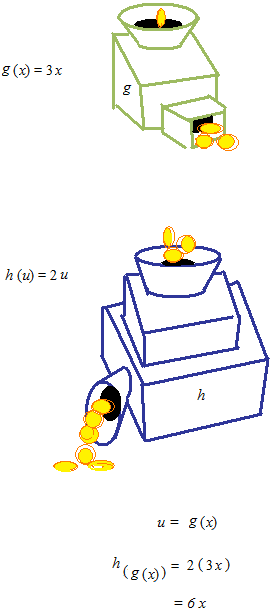
Chain rule can be represented by a figure like this. Differentiation with chain rule.
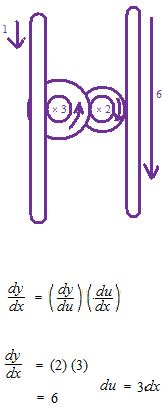
If the variable is the height of a volume.
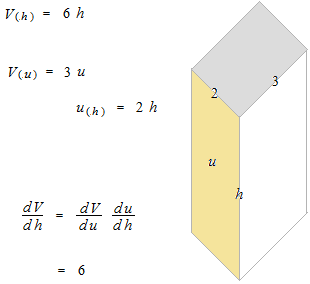
Each one of these two big right triangles is independent. Tangent is the proportion of the height of right triangle to its base. Each one has its 1 of different value.
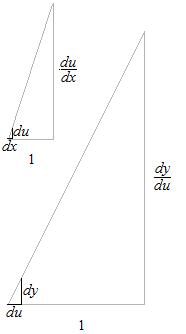
Between these two functions g(x) , h(u) , we can think as if there is a difference of width of graduations. The interior function determines the relative measure of the graduations of the coordinates of the exterior function.
When you have a function which is a little bit complicated, you can decompose it into two or more more simple functions. You will be able to consider a function as a composite function of two or more functions.
If you have a function and change this function into a composite function of two functions, you will have three functions in all. For a while, only composition of two functions will be mentioned.
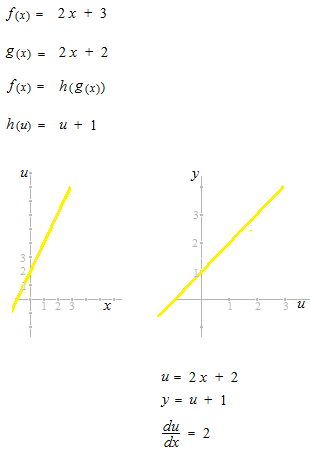
Let’s see these graphs.
As du is twice as long as dx, the unit “1” of the coordinates u-y is twice as long as the unit in u – y .
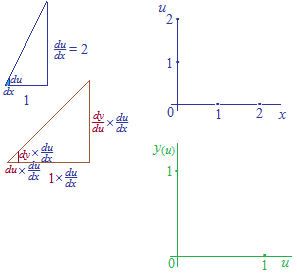
Each graph of two functions of a composite function is on the coordinates of different scales of unit width “1”.
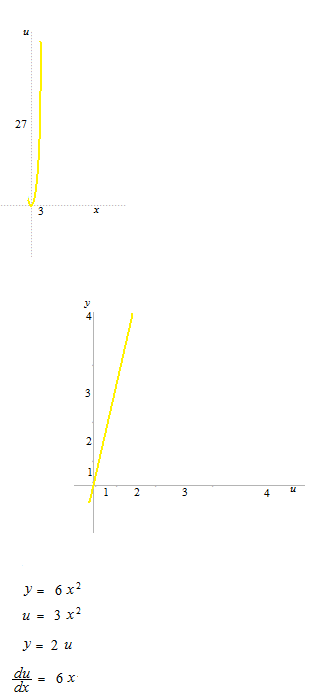
The graduations of the coordinates of the outside function are not regular, unless the inside function is linear.
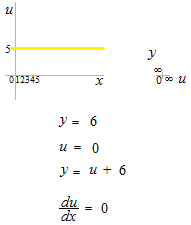
If you make a composite function from a constant function with chain rule, you will have denominator du = 0.
