Appendix; A classical therapy for panic disorder and phobia
This page presents you a symptomatic therapy without medication that is effective for panic disorder, agoraphobia, phobia, etc. This is a very classical, non-Freudian therapy, already known to everyone, such as the therapy of Claire Weekes. This therapy is not included in the Kuriki method, which is an etiological therapy for Tourette’s syndrome and obsessive-compulsive disorder. Also, the content of this page is not included in the e-book version of the “Kuriki method” either. This is a very superficial symptomatic therapy, which can be easily understood with an immediate effect. This is a description for patients with panic disorder who want to heal as quickly as possible, for example, to go to work in a crowded train or a crowded bus, however this is not a therapy for neurosis. (A therapy of neurosis by the Kuriki method must take at least three months. Cf., the Kuriki method, §41 Etiological therapy for panic disorder)
First of all, a medical examination (internal) with a blood test is indispensable.
Panic disorder is a trap: the patient will be get out of it as discovering its mechanism. The cure of panic disorder is nothing other than the patient’s understanding of this mechanism.
Also, if the symptoms of a phobia manifest bodily, a cure will be done in the same manner.
Mechanism of panic disorder
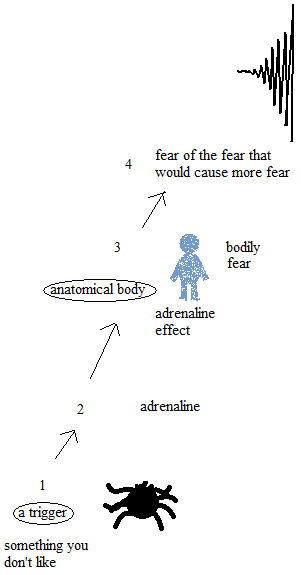
Trigger
A thing or a situation that you don’t like may be a trigger of panic attack. Anything can be a trigger of panic disorder, if you don’t like it. It is just a trigger, and you don’t need to categorize the disease of panic disorder by the types of triggers. There is no panic attack without trigger, i. e., the trigger may be the thought that a thought on possibility of panic attack can be a trigger. (Agoraphobia, etc.)
Secretion of adrenaline
There is a natural defense mechanism in our body; self-preservation. Whether to fight with the enemy or to escape from the situation, our body starts to prepare for the effort by secreting adrenaline from the adrenal glands. The adrenaline circulates the whole body by the blood within seconds. (Cf., fight-or-flight response)
You must know exactly where the adrenal glands are.

The changes in bodily state by an adrenaline secretion.
Immediately, various effects of adrenaline occur on the whole body. It’s just like before running a 100 meters or jumping into a swimming pool, the tension manifests physically as an urgent reaction. The adrenal glands secrete adrenaline directly into the blood, and adrenaline flows rapidly throughout the body. It’s so fast that when you feel adrenaline rising, the effects of adrenaline are already at their maximum level. The effects of adrenaline can not go any further. The body of each person has its personal hormonal reactions and each person has always the same adrenaline-reactions, because it is a matter of chemistry.
Some examples of the adrenaline effects
· slight tension in the muscles of various parts of the body; arms, legs, mouth, throat, stomach, belly, etc.,
· perspiration on the forehead,
· dry mouth, dry tongue,
· need to breathe more,
· sweaty hands,
· change in heartbeat,
· blood pressure up or down, etc., etc.
Fear
Fear is a bodily reaction. The emotion of fear is an alarm, a bodily preparation and a secretion of adrenaline facing danger. Fear is essential for the survival of a living organism.
You want to get out of the place: it is adrenaline that commands you to find an exit. A place of which you will not be able to get out easily is unpleasant for you.
Fear of the change of the body state.
Instead of recognizing each one of the effects of adrenaline separately, you take them, in error, for a whole of large feeling. You think there is “something” that is not going well in your body. For example, instead of recognizing a tension in the muscles of your arms, you think “something” very bad starts in your entire body. Instead of recognizing the decrease in saliva in your mouth, you think as though your whole body are betraying you.
At that time, the object of phobia is no longer the thing you don’t like, the trigger, but the state of your body; this instability of the body, which betrays you.
(When you want to breathe more, you should breathe as less as possible. The people who do not know it do deep breathing in error. Cf., Hyperventilation, Respiratory alkalosis)
Fear of the coming deterioration of the bodily state
You think, in error, that the bodily state will get worse in two seconds. It is the fear of the change in the bodily state. The sensation of urgency in anticipation of bodily deterioration under the effects of adrenaline, as much mental as physical. At that time, the object of the fear is a coming bodily state. This coming state is unknown to you, and that is why you can be afraid of it.
However, it is not all. Unless it is a physically very uncomfortable place, the problem is that you know that the cause of this sensation of urgency is a mental recognition, such as “this place has no exit.”
Fear of fear; Phobophobia
As fear is the cause of this deterioration of the bodily state, you are afraid of a greater fear, which will cause a greater deterioration of the bodily state. Your mind tries to remain quiet, but it is fear of fear that the body can have. Fear is a bodily reaction.
Amplification of fear
Fear can amplifies itself by the fear that a greater bodily fear would make a greater bodily fear. This fear is false. False, because the object of the fear is empty, as fear itself: the object of fear is fear. This amplification is the panic. As a laser beam, which is reflected in a mirror box and grows up, this bodily sensation of urgency is growing by itself and in itself. You feel as water begins to boil, or a strong burning bodily sensation.
Also, you do not want to be seen by others in a suffocated state.
The falsity of fear

Cure for panic disorder
Now, what you must do is enumerate all the adrenaline reactions that your body has at the moment of panic. The effects of adrenaline are strong, but there are also some effects of adrenaline very subtle to recognize. These effects might be very subtle to notice, but the vague totality of these effects, which were not clearly recognized one by one, gave you a very bad urgent sensation as a whole. What you must do now is check them up all, one by one, enumerate all the effects that adrenaline secretion makes upon your body. Make a list of them, at least mentally, better on a paper one by one,(recommended). There must be about twenty. If it happens that you get a panic the next time, it will be the occasion to check if your list is complete or not. Your fault was that you did not observe each adrenaline effect separately on each part of the body. You took all the effects all together and you thought only about what would happen in two seconds and thought it was going to increase further. The cause of this feeling was the set of all little changes that were found throughout your body. In fact, a panic of phobia is a phobia of panic. Phobia itself is the object of phobia, and panic itself is the object of panic.
It is a mistake to interpret normal effects of adrenaline as abnormal, though it is the body state of all children in playground. The maximum value of fear is the maximum value of adrenaline effects. Fear must be recognized at the physical level, in the same way as pain. Everyone is afraid of something, such as spiders, etc., but you do not need to confuse “the feeling of a change in blood pressure” and “fear”. In other words, you must know that “fear” is “the feeling of a change in blood pressure”.